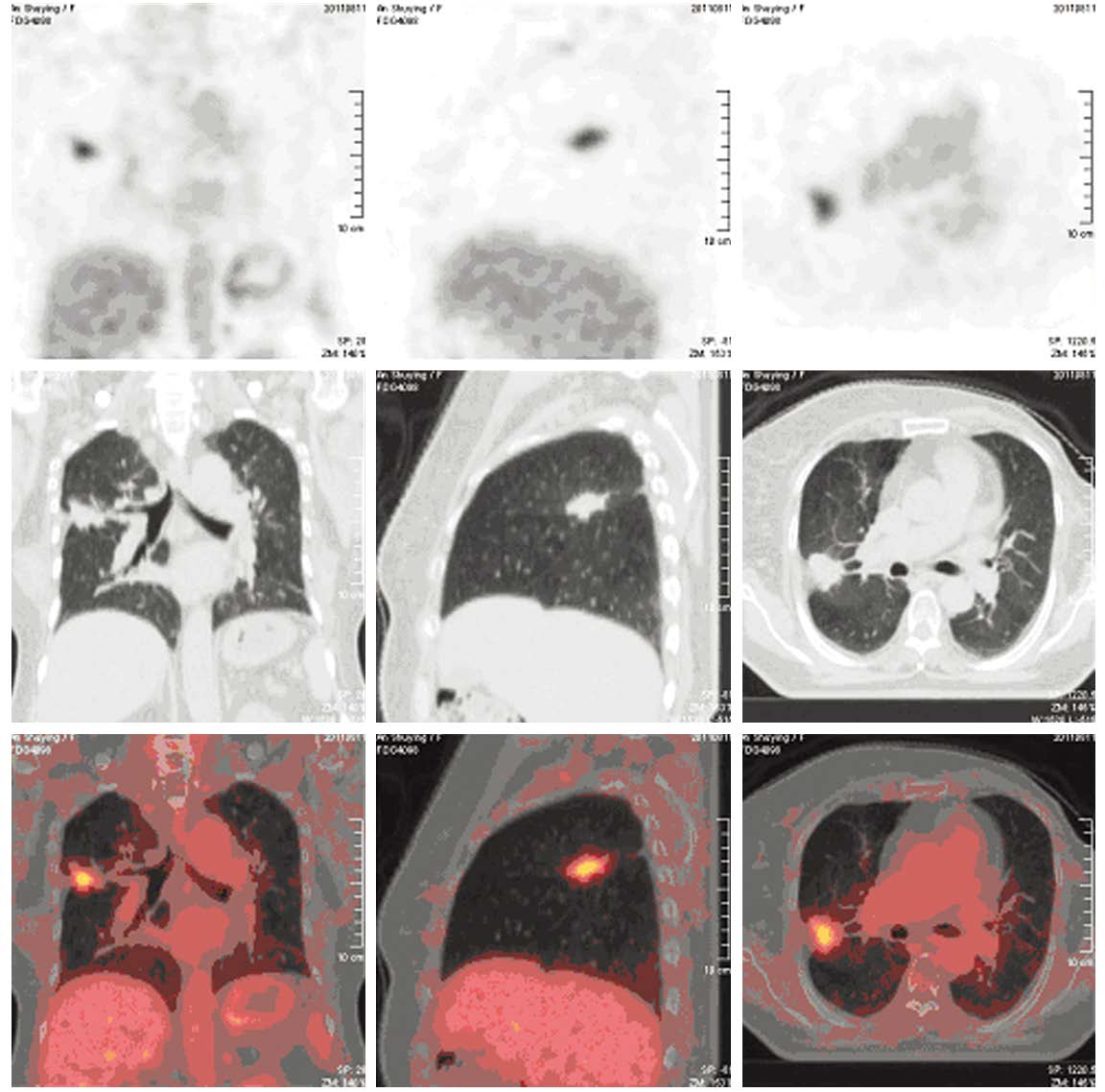
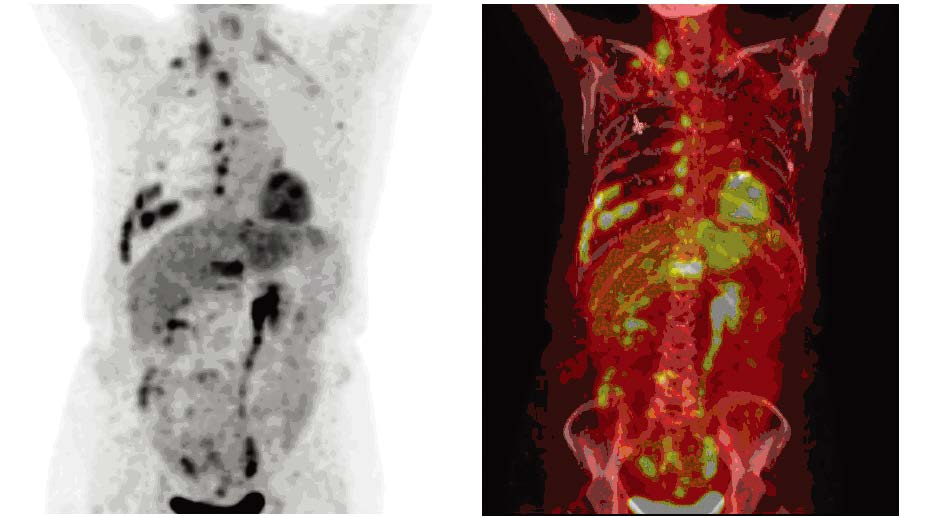
Application of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Follow-up of Primary Breast Cancer Patients with Increased Serum CEA and(or) CA153
-
摘要:目的
通过对56例乳腺癌治疗后CEA和(或)CA153升高病例的回顾性分析,了解18F-FDGPET/CT此类患者复发转移诊断方面的临床应用价值。
方法发现血清CEA和(或)CA153升高后3天至1月内行常规18F-FDG PET/CT显像。由三名有多年诊断经验的医师独立阅片,有两名及以上医师意见一致时方可做出诊断。以病理结果或随访一年结果作为诊断金标准。
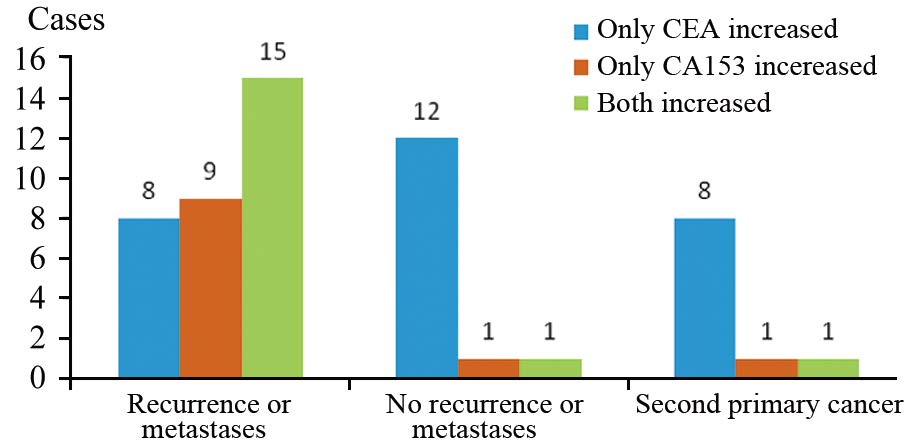
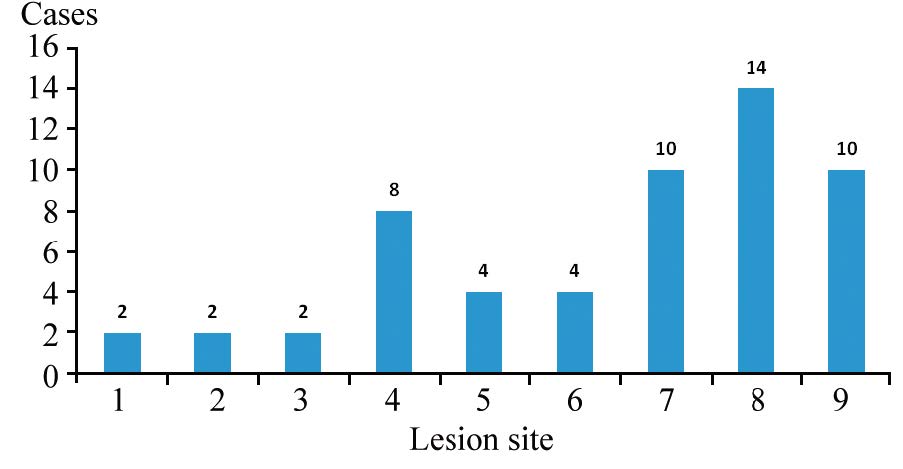
结果56例患者确诊局部复发2例、转移30例、无复发转移14例、第二原发癌10例。18F-FDG PET/CT显像阳性者41例(假阳性1例)、阴性者15例(假阴性病例2例)。其诊断敏感度95.24%,特异性92.86%,准确性94.64%,假阴性率4.76%,假阳性率7.14%,PPV 97.56%, NPV 86.67%。单纯CEA升高、单纯CA153升高及二者联合升高诊断阳性预测值(PPV)分别为:57.14%、90.91%和94.12%,其差异有统计学意义(χ2=10.430, P=0.005)。
结论乳腺癌治疗后随访期间出现CEA和(或)CA153升高的患者, 18F-FDG PET/CT显像可以准确识别或排除复发转移,还可以发现第二原发癌,具有较高的诊断效能和较好的临床应用价值。
-
关键词:
- 乳腺癌 /
- 正电子发射计算机断层显像 /
- 肿瘤标志物
Abstract:ObjectiveTo understand the application value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis of recurrenceand metastasis of breast cancer patients with increased serum CEA and/or CA153 after treatment.
Methods18F-FDG PET/CT images of 56 breast cancer patients who underwent surgery with or without chemotherapyor radiotherapy were acquired in three days to one month after increased serum CEA and(or) CA153 werefound. Diagnoses were made by the consistent comment of two or more doctors after three experiencednuclear medicine doctors reviewed the images retrospectively and independently. And the gold standard ofdiagnoses were the results of either pathology or one-year follow-up.
ResultsOf all 56 cases, there were twocases of local recurrence, 30 cases of metastasis, 14 cases without recurrence and 10 cases of second primarytumor. 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging was positive in 41 cases (one false positive case), negative in 15 cases (twofalse negative cases). The diagnostic efficiency of 18F-FDG PET/CT were: sensitivity 95.24%, specificity92.86%, accuracy 94.64%, false negative rate 4.76%, false positive rate 7.14%, positive predictive value(PPV) 97.56%, and negative predictive value (NPV) 86.67%. The PPV of increased CEA alone, increasedCA153 alone and their combination were 57.14%, 90.91% and 94.12%, respectively (χ2=10.430, P=0.005).
Conclusion18F-FDG PET/CT can be used to identify or rule out the recurrence and metastasis in breastcancer patients with increased serum CA153 and(or) CEA after treatment, with high diagnostic efficiency andgood clinical application value. And it can also suggest the second primary tumor.
-
Key words:
- Breast cancer /
- PET/CT /
- Tumor marker
-
-
表 1 18F-FDG PET/CT显像的诊断效能
Table 1 Diagnostic efficiency of 18F-FDG PET/CT

表 2 18F-FDG PET/CT显像阳性对PPV的作用
Table 2 Effect of positive 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging on PPV

-
[1] Bernard WS, Christopher PW. World Cancer Report 2014[M].Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2014:509-27.
[1] Bernard WS, Christopher PW. World Cancer Report 2014[M]. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2014: 50 9-27. [2] Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, et al. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28(20): 3271-7. [2] Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, et al. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2010, 28(20): 3271-7.
[3] Berman AT, Thukral AD, Hwang WT, et al. Incidence and patterns of distant metastases for patients with early stage breast cancer after breast conservation treatment[J]. Clin Breast Cancer, 2013,13(2): 88-94.
[3] Berman AT, Thukral AD, Hwang WT, et al. Incidence and patterns of distant metastases for patients with early stage breast cancer after breast conservation treatment[J]. Clin Breast Cancer, 2013, 13 (2): 88-94. [4] Evangelista L, Cervino AR, Ghiotto C, et al. Tumor marker-guided PET in breast cancer patients-a recipe for a perfect wedding: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 20 12, 37(5): 467-74. [4] Evangelista L, Cervino AR, Ghiotto C, et al. Tumor marker-guided PET in breast cancer patients-a recipe for a perfect wedding: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Nucl Med,2012, 37(5): 467-74.
[5] Bourgeois AC,Warren LA,Chang TT, et al. Role of positron emission tomography/computed Tomography in breast cancer[J]. Radiol Clin North Am, 2013, 51(5) :781-98. [5] Bourgeois AC,Warren LA,Chang TT, et al. Role of positron emission tomography/computed Tomography in breast cancer[J].Radiol Clin North Am, 2013, 51(5) :781-98.
[6] Stieber P, Nagel D, Blankenburg I, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of CA 15 -3 and CEA in the early detection of metastatic breast cancer-A retrospective analysis of kinetics on 743 breast cancer patients[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2015, 448: 228-31. [6] Stieber P, Nagel D, Blankenburg I, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of CA 15-3 and CEA in the early detection of metastatic breast cancer-A retrospective analysis of kinetics on 743 breast cancer patients[J].Clin Chim Acta, 2015, 448: 228-31.
[7] Khatcheressian JL, Hurley P, Bantug E, et al. Breast cancer followup and management after primary treatment: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2013, 31(7): 961-5.
[7] Khatcheressian JL, Hurley P, Bantug E, et al. Breast cancer followup and management after primary treatment: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2013, 31(7): 961-5. [8] Champion L, Brain E, Giraudet AL, et al. Breast cancer recurrence diagnosis suspected on tumor marker rising: value of whole-body 18 FDG-PET/CT imaging and impact on patient management[J]. Cancer, 2011, 117(8): 1621-9. [8] Champion L, Brain E, Giraudet AL, et al. Breast cancer recurrence diagnosis suspected on tumor marker rising: value of whole-body 18FDG-PET/CT imaging and impact on patient management[J].Cancer, 2011, 117(8): 1621-9.
[9] Chen JW, Wang J, Liu B, et al. Impact of 18F-FDG PET/CT compared with diagnostic CT on following-up breast cancer after surgery[J]. Nanjing Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao(Zi Ran Ke Xue Ban), 20 10, 30(2): 195-8. [陈建伟, 王杰, 刘标, 等. PET/CT与胸部诊 断CT在乳腺癌术后随访中的比较[J].南京医科大学学报(自然 科学版) , 2010, 30(2): 195-8.] [9] 陈建伟, 王杰, 刘标, 等. PET/CT与胸部诊断CT在乳腺癌术后随访中的比较[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 30(2): 195-8. Chen JW, Wang J, Liu B, et al. Impact of 18F-FDG PET/CT compared with diagnostic CT on following-up breast cancer after surgery[J]. Nanjing Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao(Zi Ran Ke Xue Ban),2010, 30(2): 195-8.



 下载:
下载: