Expression and Significance of TNF-α and TNFR1 in Human Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tissues
-
摘要:目的
探讨不同病理类型宫颈组织中TNF-α和TNFR1的表达及其与宫颈鳞癌之间的关系。
方法应用实时定量RT-PCR法检测正常宫颈(正常组,48例)、宫颈上皮内瘤样病变(CIN组,47例)和宫颈鳞癌(SCC组,39例)组织中TNF-α和TNFR1、TNFR2 mRNA表达水平,采用免疫组织化学SP法检测TNF-α蛋白表达,Western blot法检测TNFR1、TNFR2蛋白表达,将TNF-α和TNFR1 mRNA表达结果与临床病理结果进行相关性分析。
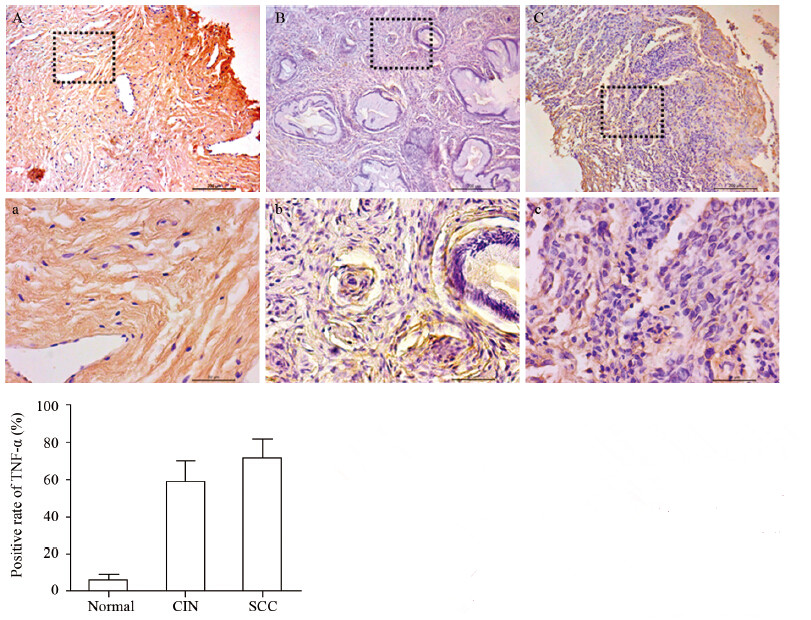
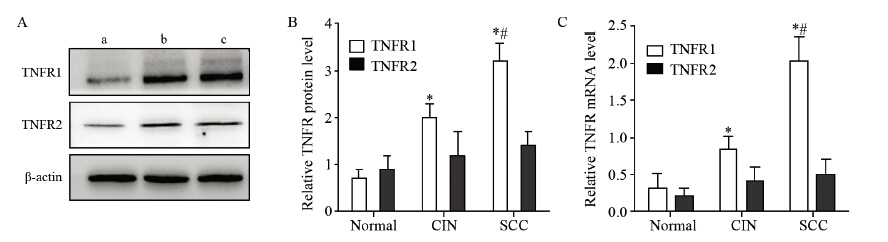
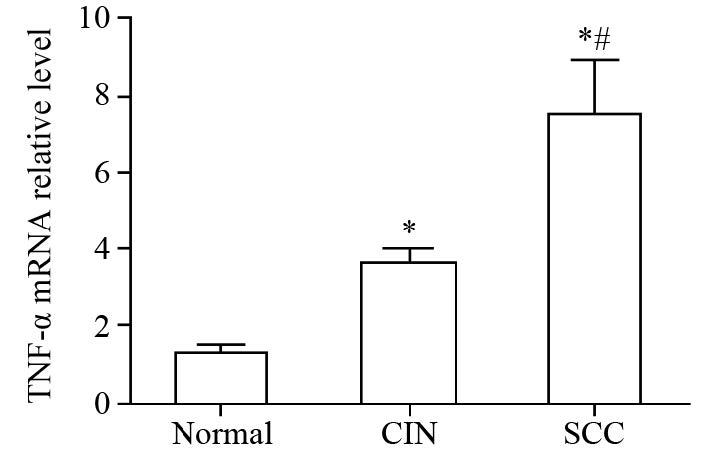
结果TNF-α和TNFR1的mRNA表达水平随宫颈癌变程度的增加而升高,组间两两比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),而TNFR2在各组中的表达差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);TNF-α在宫颈组织中的表达随病理程度的增加有显著升高,正常组为6.25%、CIN组为58.82%、SCC组为71.79%,组间比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);TNFR1蛋白表达水平随宫颈癌变程度的增加而升高,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),TNFR2在各组中的表达变化不明显,均与其mRNA在各组间的表达结果一致;SCC组中的TNF-α和TNFR1 mRNA的表达量与肿瘤大小、临床分期、浸润深度以及淋巴结转移情况呈正相关性,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),与患者年龄以及细胞分化程度无关。
结论TNF-α和TNFR1的激活与宫颈鳞癌的发生、发展相关,参与肿瘤微环境的变化,两者将有望成为治疗宫颈鳞癌的靶标。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the expression of TNF-α and TNFR1 in cervix tissues with differentpathological types and their relationship with cervical squamous cell carcinoma(SCC).
MethodsRealtimeRT-PCR was performed to determine the mRNA levels of TNF-α, TNFR1, and TNFR2 in normal cervixgroup (n=48), cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) group (n=47) and SCC group (n=39). The protein levelsof TNFR1 and TNFR2 in cervical tissues were assessed by Western blot. Immunohistochemistry was used todetermine TNF-α expression in cervical tissues. The correlation of TNF-α and TNFR1 mRNA expression withcervical pathological types were also investigated.
ResultsThe mRNA levels of TNF-α and TNFR1 wereprogressively increased with the increasing grade of carcinoma (P<0.05), whereas the difference of TNFR2mRNA expression in the three groups was not statistically significant (P>0.05). The expression of TNF-αwas also progressively increased with the increasing grade of carcinoma, and the proportion of positive cellsin normal cervix group, CIN group and SCC group were 6.25%, 58.82% and 71.79%, respectively (P<0.01).The protein level of TNFR1 was progressively increased with the increasing grade of carcinoma (P<0.01),whereas the TNFR2 expression was unchanged. Moreover, the positive correlations were found betweenTNF-α or TNFR1 mRNA levels in SCC group and tumor size, clinical stages, invasive depth, lymphaticmetastasis(P<0.05), instead of age and differentiation degree.
ConclusionThe activation of TNF-α andTNFR1 may play a critical role in the initiation and progression of cervical carcinoma by contributing to thechanges of cancer microenvironment, which are potential therapeutic targets of SCC.
-
Key words:
- Cervical squamous cell carcinoma /
- TNFR1 /
- TNF-α
-
-
表 1 TNF-α及GAPDH引物序列信息
Table 1 TNF-α and GAPDH primer sequence

表 2 TNF-α和TNFR1 mRNA表达与宫颈鳞癌临床病理特征的关系 (2-ΔΔCt,x±s)
Table 2 Relationship between TNF-α,TNFR1 mRNAexpression and clinicopathological features of cervicalsquamous cell carcinoma (2-ΔΔCt,x±s)

-
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65(1): 5-29. [1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015[J]. CACancer J Clin, 2015, 65(1): 5-29.
[2] Gillison ML, Castellsagué X, Chaturvedi A, et al. EuroginRoadmap: comparative epidemiology of HPV infection andassociated cancers of the head and neck and cervix[J]. Int J Cancer, 2014, 134(3): 497-507.
[2] Gillison ML, Castellsagué X, Chaturvedi A, et al. Eurogin Roadmap: comparative epidemiology of HPV infection and associated cancers of the head and neck and cervix[J]. Int J Cancer, 2014, 134(3): 497-507. [3] Fernandes JV, Medeiros Fernandes TA, DE Azevedo JC, et al. Linkbetween chronic inflammation and human papillomavirus-induced carcinogenesis (Review)[J]. Oncol Lett, 2015, 9(3): 1015-26.
[3] Fernandes JV, Medeiros Fernandes TA, DE Azevedo JC, et al. Link between chronic inflammation and human papillomavirus-induced carcinogenesis (Review)[J]. Oncol Lett, 2015, 9(3): 1015-26. [4] Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M. Regulation and function of NFkappaBtranscription factors in the immune system[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2009, 27: 693-733.
[4] Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M. Regulation and function of NFkappaB transcription factors in the immune system[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2009, 27: 693-733. [5] Gerondakis S, Grumont R, Gugasyan R, et al. Unravelling thecomplexities of the NF-κB signalling pathway using mouse knockout and transgenic models[J]. Oncogene, 2006, 25(51):6781-99.
[5] Gerondakis S, Grumont R, Gugasyan R, et al. Unravelling the complexities of the NF-κB signalling pathway using mouse knockout and transgenic models[J]. Oncogene, 2006, 25(51): 67 81-99. [6] Popivanova BK, Kitamura K, Wu Y, et al. Blocking TNF-α inmice reduces colorectal carcinogenesis associated with chronic colitis[J]. J Clin Invest, 2008, 118(2): 560-70.
[6] Popivanova BK, Kitamura K, Wu Y, et al. Blocking TNF-α in mice reduces colorectal carcinogenesis associated with chronic colitis[J]. J Clin Invest, 2008, 118(2): 560-70. [7] Oshima H, Ishikawa T, Yoshida GJ, et al. TNF-α/TNFR1 signaling promotes gastric tumorigenesis through induction of Noxo1 and Gna14 in tumor cells[J]. Oncogene, 2014, 33(29): 3820-9. [7] Oshima H, Ishikawa T, Yoshida GJ, et al. TNF-α/TNFR1 signalingpromotes gastric tumorigenesis through induction of Noxo1 and Gna14 in tumor cells[J]. Oncogene, 2014, 33(29): 3820-9.
[8] Tomita Y, Yang X, Ishida Y, et al. Spontaneous regression of lung metastasis in the absence of tumor necrosis factor receptor p55[J].Int J Cancer, 2004, 112(6): 927-33.
[8] Tomita Y, Yang X, Ishida Y, et al. Spontaneous regression of lung metastasis in the absence of tumor necrosis factor receptor p55[J]. Int J Cancer, 2004, 112(6): 927-33. [9] Yang YF, Jan YH, Liu YP, et al. Squalene synthase induces tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 enrichment in lipid rafts to promote lung cancer metastasis[J]. Am J Respir Criti Care Med, 2014, 190(6): 67 5-87. [9] Yang YF, Jan YH, Liu YP, et al. Squalene synthase induces tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 enrichment in lipid rafts to promote lung cancer metastasis[J]. Am J Respir Criti Care Med, 2014, 190(6):675-87.
[10] Nakayama S, Yokote T, Tsuji M, et al. Expression of tumour necrosis factor-α and its receptors in Hodgkin lymphoma[J]. Br J Haematol, 2014, 167(4): 574-7. [10] Nakayama S, Yokote T, Tsuji M, et al. Expression of tumour necrosis factor-α and its receptors in Hodgkin lymphoma[J]. Br J Haematol, 2014, 167(4): 574-7.
[11] Chiechi A, Novello C, Magagnoli G, et al. Elevated TNFR1 and serotonin in bone metastasis are correlated with poor survival following bone metastasis diagnosis for both carcinoma and sarcoma primary tumors[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2013, 19(9): 24 73-85. [11] Chiechi A, Novello C, Magagnoli G, et al. Elevated TNFR1 andserotonin in bone metastasis are correlated with poor survivalfollowing bone metastasis diagnosis for both carcinoma and sarcoma primary tumors[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2013, 19(9):2473-85.
[12] Zhu G, Du Q, Wang X, et al. TNF-α promotes gallbladder cancer cell growth and invasion through autocrine mechanisms[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2014, 33(6): 1431-40. [12] Zhu G, Du Q, Wang X, et al. TNF-α promotes gallbladder cancercell growth and invasion through autocrine mechanisms[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2014, 33(6): 1431-40.
[13] Xia L, Xue XZ. Immunohistochemical study of NF-κB p65, c-IAP2and caspase-3 expression in cervical cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2012, 3(4): 839-44.
[13] Xia L, Xue XZ. Immunohistochemical study of NF-κB p65, c-IAP2 and caspase-3 expression in cervical cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2012, 3( 4): 839-44. [14] Wajant H, Scheurich P. TNFR1-induced activation of the classical NF-κB pathway[J]. FEBS J, 2011, 278(6): 862-76. [14] Wajant H, Scheurich P. TNFR1-induced activation of the classicalNF-κB pathway[J]. FEBS J, 2011, 278(6): 862-76.[15] Rivas MA, Carnevale RP, Proietti CJ, et al. TNF alpha acting onTNFR1 promotes breast cancer growth via p42/P44 MAPK, JNK,Akt and NF-kappa B-dependent pathways[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2008,314(3): 509-29.
[15] Rivas MA, Carnevale RP, Proietti CJ, et al. TNF alpha acting on TNFR1 promotes breast cancer growth via p42/P44 MAPK, JNK,Akt and NF-kappa B-dependent pathways[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2008,314(3): 509-29.
[15] Rivas MA, Carnevale RP, Proietti CJ, et al. TNF alpha acting on TNFR1 promotes breast cancer growth via p42/P44 MAPK, JNK, Akt and NF-kappa B-dependent pathways[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2008, 31 4(3): 509-29. [16] Ji H, Cao R, Yang Y, et al. TNFR1 mediates TNF-α-inducedtumour lymphangiogenesis and metastasis by modulating VEGFC-VEGFR3 signalling[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 4944
[16] Ji H, Cao R, Yang Y, et al. TNFR1 mediates TNF-α-induced tumour lymphangiogenesis and metastasis by modulating VEGFC- VEGFR3 signalling[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 4944.



 下载:
下载: