Inhibitory Effect of Thermosensitive Liposomes Combined with Microwave Thermotherapy on Human Cervical Carcinoma Cells HeLa
-
摘要:目的
构建阿霉素热敏脂质体(DOX-TSLs),并研究其与微波热疗联合对人宫颈癌HeLa细胞的治疗作用。
方法使用逆向蒸发法制备DOX-TSLs;检测其包封率及体外热敏释放情况;MTT法检测HeLa细胞在化疗、热疗及联合治疗时的存活率;流式细胞术检测联合治疗时的细胞凋亡情况。
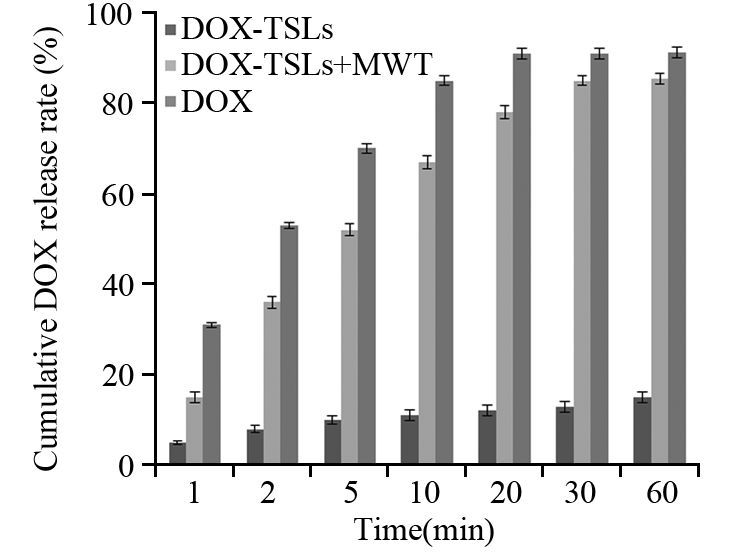
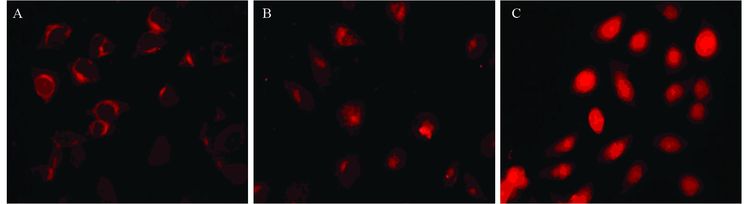
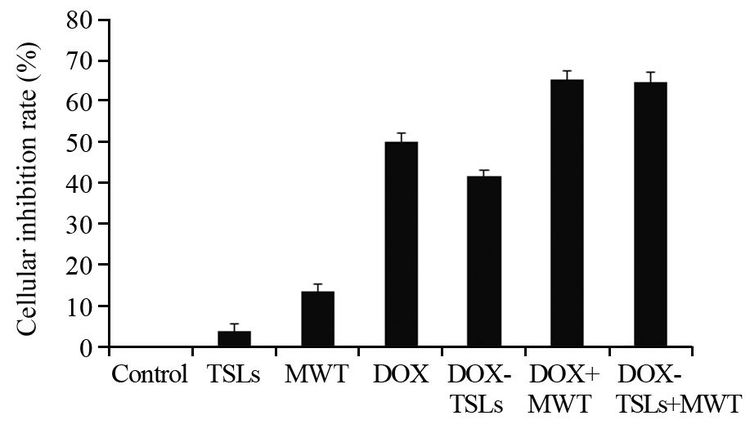
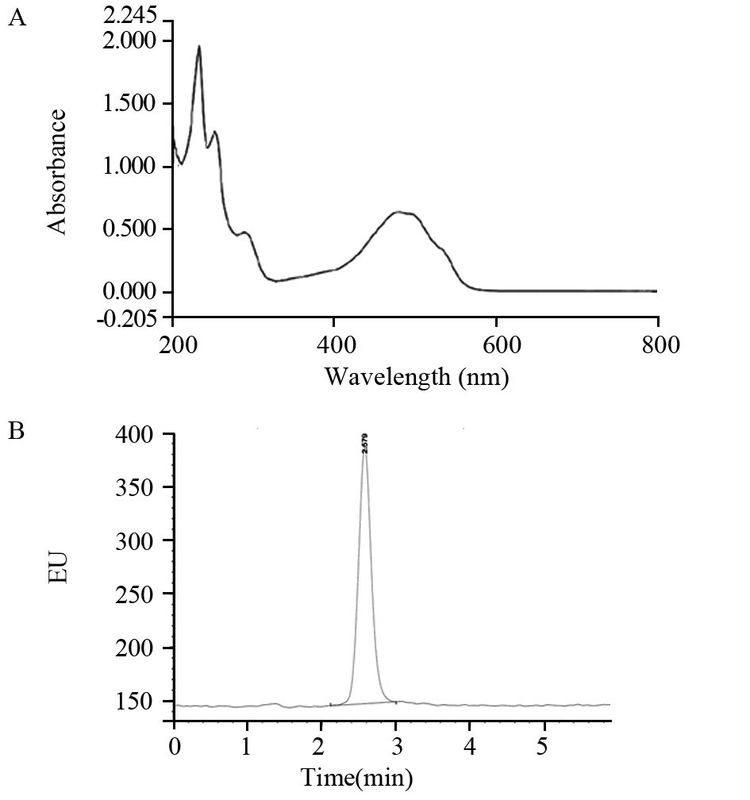
结果成功构建DOX-TSLs,平均粒径为(190.7±4.8)nm,包封率88.5%;体外累积释放率实验结果表明,DOX-TSLs可在微波热疗条件下迅速释放药物,30 min药物累积释放率达85%以上;DOX-TSLs可在6 h内完全进入肿瘤细胞内部;DOX-TSLs与微波热疗联合可有效抑制肿瘤细胞增殖;与热疗联合能促进细胞凋亡,联合治疗时细胞凋亡率为(62.2±2.3)%。
结论DOX-TSLs与微波热疗联合治疗人宫颈癌HeLa细胞具有明显协同作用,为宫颈癌的治疗模式提供了新的理论及实验依据。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo construct the thermos-sensitive liposomes loading with doxorubicin drug delivery system (DOX-TSLs) and investigate the effect of its combination with microwave thermotherapy on human cervical carcinoma cells HeLa in vitro.
MethodsReverse evaporation method was used to prepare DOXTSLs; drug loading rate and in vitro release were detected; MTT method was used to detect the inhibition of HeLa cells treated with chemotherapy, thermotherapy and the combination; the apoptosis rate was detected by flow cytometry.
ResultsDOX-TSLs drug delivery system was constructed successfully with the average particles size (190.7±4.8) nm and the efficiency 88.5%; the in vitro release detection revealed that the cumulative release rate could reach 85% with microwave thermotherapy at 30 min; DOX could be delivered into HeLa cells within 6 h by DOX-TSLs; the combination therapy of DOX-TSLs and microwave thermotherapy could inhibit cell proliferation effectively and significantly promote cell apoptosis which could be reach (62.2±2.3) %.
ConclusionDOX-TSLs combined with microwave thermotherapy in the treatment of human cervical carcinoma cells HeLa have a synergistic effect. This therapy provides newly theoretical and experimental basis of human cervical carcinoma.
-
Key words:
- TSLs /
- Microwave /
- Thermotherapy /
- Combination therapy
-
-
-
[1] Bassal R, Schejter E, Bachar R, et al. Recent trends of cervical cancer and Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia 3(CIN3) in Israel[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2015, 292(2): 405-13. [1] Bassal R, Schejter E, Bachar R, et al. Recent trends of cervical cancer and Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia 3(CIN3) in Israel[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2015, 292(2) : 405-13.
[2] Touboul C, Skalli D, Guillo E, et al. Treatment of cervical cancer[J]. Rev Prat, 2014, 64(6): 802-6. [2] Touboul C, Skalli D, Guillo E, et al. Treatment of cervical cancer[J]. Rev Prat, 2014, 64(6) : 802-6.
[3] Sato I, Umemura M, Mitsudo K, et al. Hyperthermia generated with ferucarbotran (Resovist(A (R))) in an alternating magnetic field enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis of cultured human oral cancer cells[J]. J Physiol Sci, 2014, 64(3): 177-83. [3] Sato I, Umemura M, Mitsudo K, et al. Hyperthermia generated with ferucarbotran (Resovist(A (R))) in an alternating magnetic field enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis of cultured human oral cancer cells[J]. J Physiol Sci, 2014, 64(3) : 177-83.
[4] Shi H, Liu T, Fu C, et al. Insights into a microwave susceptible agent for minimally invasive microwave tumor thermal therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 44: 91-102.
[4] Shi H, Liu T, Fu C, et al. Insights into a microwave susceptible agent for minimally invasive microwave tumor thermal therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 44: 91-102. [5] Tropea A, Biondi A, Corsaro A, et al. Combined microwave thermal ablation and liver resection for single step treatment of otherwise unresectable colorectal liver metastases; a monoistitutional experiences[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 20 14, 18(2 Suppl): 6-10. [5] Tropea A, Biondi A, Corsaro A, et al. Combined microwave thermal ablation and liver resection for single step treatment of otherwise unresectable colorectal liver metastases; a monoistitutional experiences[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2014, 18(2 Suppl): 6-10.
[6] Sun F, Yin LF, Zhou JP. Current advances in study of thermosensitive liposomes[J]. Yao Xue Jin Zhan, 2010, 34(9): 39 9-405. [孙飞, 尹莉芳, 周建平. 热敏脂质体的研究进展[J]. 药 学进展, 2010, 34(9): 399-405.] [6] 孙飞, 尹莉芳, 周建平. 热敏脂质体的研究进展[J]. 药学进展, 2010, 34(9) : 399-405. Sun F, Yin LF, Zhou JP. Current advances in study of thermosensitive liposomes[J]. Yao Xue Jin Zhan, 2010, 34(9) : 399-405.
[7] Mohammad F, Yusof NA. Doxorubicin-loaded magnetic gold nanoshells for a combination therapy of hyperthermia and drug delivery[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2014, 434: 89-97. [7] Mohammad F, Yusof NA. Doxorubicin-loaded magnetic gold nanoshells for a combination therapy of hyperthermia and drug delivery[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2014, 434: 89-97.
[8] Chen YT, Yao HR, Xu LF, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with endogenetic hyperthermia treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 2014, 61 (129): 151-5. [8] Chen YT, Yao HR, Xu LF, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy combined with endogenetic hyperthermia treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 2014, 61(129) : 151-5.
[9] Lee SM, Kim HJ, Kim SY, et al. Drug-loaded gold plasmonic nanoparticles for treatment of multidrug resistance in cancer[J]. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(7) : 2272-82.
[9] Lee SM, Kim HJ, Kim SY, et al. Drug-loaded gold plasmonic nanoparticles for treatment of multidrug resistance in cancer[J]. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(7): 2272-82. [10] Zhang Z, Wang J, Nie X, et al. Near infrared laser-induced targeted cancer therapy using thermoresponsive polymer encapsulated gold nanorods[J]. J Am Cheml Soc, 2014, 136(20): 7317-26. [10] Zhang Z, Wang J, Nie X, et al. Near infrared laser-induced targeted cancer therapy using thermoresponsive polymer encapsulated gold nanorods[J]. J Am Cheml Soc, 2014, 136(20) : 7317-26.
[11] You J, Zhang P, Hu F, et al. Near-infrared light-sensitive liposomes for the enhanced photothermal tumor treatment by the combination with chemotherapy[J]. Pharm Res, 2014, 31(3) : 554-65.
[11] You J, Zhang P, Hu F, et al. Near-infrared light-sensitive liposomes for the enhanced photothermal tumor treatment by the combination with chemotherapy[J]. Pharm Res, 2014, 31(3): 55 4-65. [12] Kouloulias V, Triantopoulou S, Vrouvas J, et al. Combined chemoradiotherapy with local microwave hyperthermia for treatment of T3N0 laryngeal carcinoma: a retrospective study with long-term follow-up[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2014, 34(3): 16 7-73. [12] Kouloulias V, Triantopoulou S, Vrouvas J, et al. Combined chemoradiotherapy with local microwave hyperthermia for treatment of T3N0 laryngeal carcinoma: a retrospective study with long-term follow-up[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2014, 34(3) : 167-73.
[13] Zhou Y, Han G, Wang Y, et al. Radiofrequency heat-enhanced chemotherapy for breast cancer: towards interventional molecular image-guided chemotherapy[J]. Theranostics, 2014, 4(11) : 1145-52.
[13] Zhou Y, Han G, Wang Y, et al. Radiofrequency heat-enhanced chemotherapy for breast cancer: towards interventional molecular image-guided chemotherapy[J]. Theranostics, 2014, 4(11): 11 45-52. [14] DeWitt MR, Pekkanen AM, Robertson J, et al. Influence of hyperthermia on efficacy and uptake of carbon nanohorn-cisplatin conjugates[J]. J Biomech Eng, 2014, 136(2): 021003. [14] DeWitt MR, Pekkanen AM, Robertson J, et al. Influence of hyperthermia on efficacy and uptake of carbon nanohorn-cisplatin conjugates[J]. J Biomech Eng, 2014, 136(2) : 021003.
[15] Wang L, Shi J, Jia X, et al. NIR-/pH-Responsive drug delivery of functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes for potential application in cancer chemo-photothermal therapy[J]. Pharm Res, 2013, 30(11) : 2757-71.
[15] Wang L, Shi J, Jia X, et al. NIR-/pH-Responsive drug delivery of functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes for potential application in cancer chemo-photothermal therapy[J]. Pharm Res, 20 13, 30(11): 2757-71. [16] 陈万瑛, 陈钰, 杨蕊, 等. 磁性隐形阿霉素脂质体的制备及其对SKOV-3细胞影响初步研究[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2014, 18(6) : 880-3. Chen WY, Chen Y, Yang R, et al. The preparation of doxorubicinloaded Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles modified with PEG and the effect of SKOV-3 cells[J]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Zhen Duan Xue, 2014, 18(6) : 880-3.
[16] Chen WY, Chen Y, Yang R, et al. The preparation of doxorubicinloaded Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles modified with PEG and the effect of SKOV-3 cells[J]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Zhen Duan Xue, 20 14, 18(6): 880-3. [陈万瑛, 陈钰, 杨蕊, 等. 磁性隐形阿霉素脂 质体的制备及其对SKOV-3细胞影响初步研究[J]. 中国实验诊 断学, 2014, 18(6): 880-3.]



 下载:
下载: