Mechanism of LncRNA SNHG5 on Proliferation, Invasion and Apoptosis of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells by Targeting miR-421
-
摘要:目的
探讨SNHG5靶向miR-421调控多形性胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)发生与发展的分子机制。
方法收集31例GBM肿瘤与32例正常脑组织标本,实时荧光定量PCR法检测标本中SNHG5与miR-421的表达水平;通过慢病毒或质粒转染U87细胞上调或下调SNHG5的表达水平,采用实时荧光定量PCR检测转染后U87细胞中miR-421的表达水平,分析GBM中miR-421与SNHG5表达的相关性。双荧光素报告基因实验验证SNHG5对miR-421的靶向关系。利用SNHG5与miR-421两者均低表达的质粒转染U87细胞进行拯救实验,通过CCK-8、Transwell、流式细胞学分析及裸鼠体内实验验证SNHG5通过靶向miR-421调控GBM细胞增殖、侵袭及凋亡。
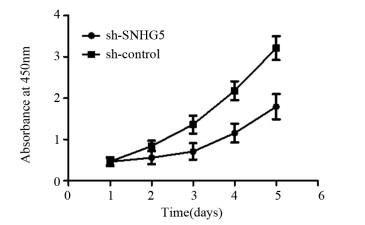
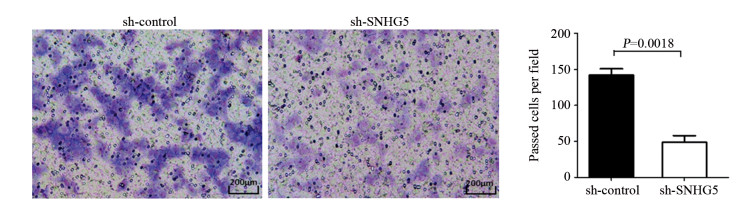
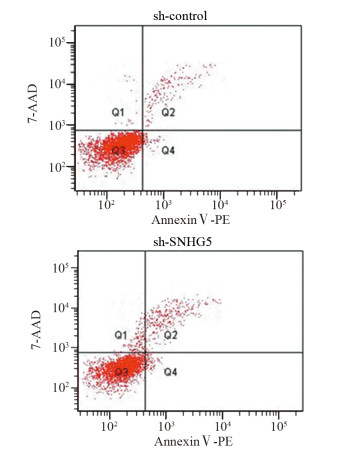
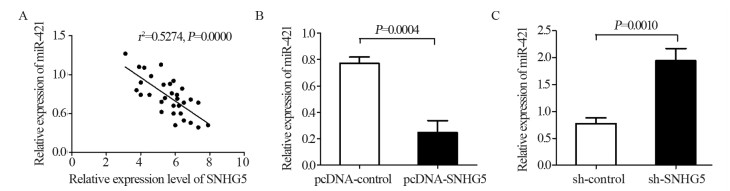
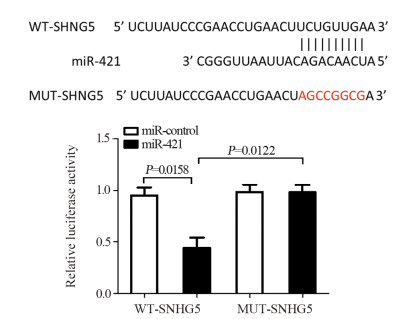
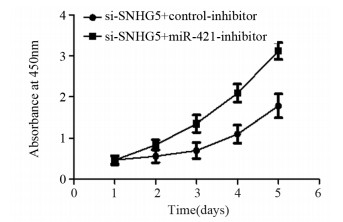
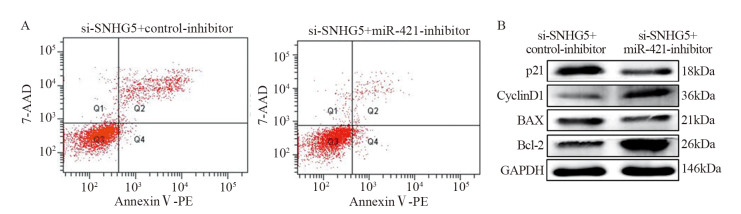
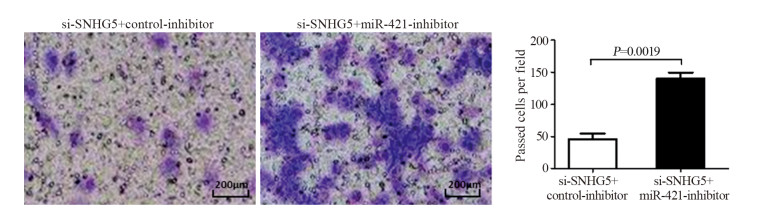
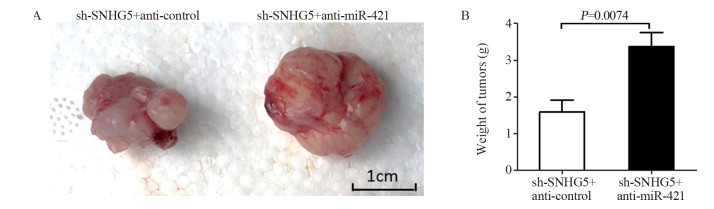
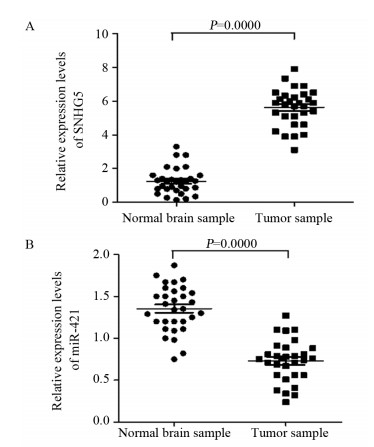
结果上调U87细胞中SNHG5表达后miR-421的表达水平显著下降,下调U87细胞中SNHG5表达后miR-421表达水平明显升高(P < 0.05),两者表达呈显著负相关。双荧光素酶报告基因实验结果提示SNHG5可靶向结合miR-421。拯救实验结果表明,相比si-SNHG5+miR-421-inhibitor组,si-SNHG5+control-inhibitor组的U87细胞增殖、侵袭及抗凋亡能力均显著下降,且BAX与p21蛋白表达水平升高,CyclinD1与Bcl-2蛋白表达显著下降(P < 0.05)。
结论SNHG5可通过靶向miR-421并影响CyclinD1、p21、BAX、Bcl-2蛋白表达进而促进GBM细胞的增殖、侵袭及抗凋亡行为。miR-421在GBM中呈低表达与SNHG5表达水平升高有关。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the molecular mechanism of SNHG5 regulating the proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells by targeting miR-421.
MethodsReal-time quantitative PCR test was performed to detect the expression levels of SNHG5 and miR-421 in 31 cases of GBM tissue samples and 32 cases of normal brain tissue samples. After increasing or decreasing SNHG5 expression in U87 cell lines by lentivirus or plasmid transfection, the changes of miR-421 expression were measured by real-time quantitative PCR, to explore the correlation between SNHG5 and miR-421 in GBM. The dual-luciferase reporter test was performed to explore the target interaction of SNHG5 and miR-421. The plasmids with low expression of SNHG5 and miR-421 were cotransfected into U87 cells for the rescue experiment. CCK-8 test, Transwell test, flow cytometry and tumor cell xenograft in nude mice were used to verify molecular mechanism of SNHG5 regulating the proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of GBM in vitro and vivo.
ResultsThe expression level of miR-421 was decreased in U87 cell line after SNHG5 upregulation. In addition, the expression level of miR-421 was increased in U87 cell line after SNHG5 downregulation (P < 0.05). The expression level of SNHG5 was correlated negatively with the expression of miR-421 in GBM and U87 cell line. The result of luciferase reporter tests indicated SNHG5 targetedly interacted with miR-421. Rescue experiment results showed that compared with si-SNHG5+miR-421-inhibitor group, the proliferation, invasion and anti-apoptosis ability of U87 cells were significantly inhibited in the si-SNHG5+control-inhibitor group, the expression levels of BAX and p21 were significantly higher, the expression levels of CyclinD1 and Bcl-2 were lower remarkably (P < 0.05).
ConclusionSNHG5 promotes the proliferation, invasion and anti-apoptosis of GBM by targeting miR-421 and regulating the expression of CyclinD1, p21, BAX and Bcl-2. Downregulation of miR-421 is related to SNHG5 overexpression in GBM.
-
Key words:
- Glioblastoma multiforme /
- SNHG5 /
- miR-421 /
- Cell proliferation
-
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:杨吉鹏:实验设计及操作、文章撰写邱翔、王同聚、李京臣:实验操作、标本收集李琛、杨建凯:实验操作焦保华:确定研究方向、实验设计及文章修改
-
-
[1] Bryukhovetskiy I, Pak O, Khotimchenko Y, et al. Personalized therapy and stem cell transplantation for pro-inflammatory modulation of cancer stem cells microenvironment in glioblastoma: Review[J]. Int Rev Neurobiol, 2020, 151: 67-98. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0074774220300234
[2] Volovat SR, Volovat C, Hordila I, et al. MiRNA and LncRNA as Potential Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Review[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 526850. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.526850
[3] Hu X, Hong Y, Shang C. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA SNHG5 inhibits malignant cellular phenotypes of glioma via Wnt/CTNNB1 signaling pathway[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(5): 1333-1340. doi: 10.7150/jca.29517
[4] Luo J, Gao Y, Lin X, et al. Systematic analysis reveals a lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network associated with dasatinib resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2021, 10(2): 1727-1738. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-343
[5] Chen Q, Hu L, Huang D, et al. Six-lncRNA Immune Prognostic Signature for Cervical Cancer[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11: 533628. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.533628
[6] Wang D, Zhang S, Zhao M, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 accelerates non-small cell lung cancer progression via regulating miR-185-5p/MDM4 axis[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(23): 9138-9149. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3570
[7] Tang Q, Li Z, Han W, et al. High expression of lncRNA SNHG1 in prostate cancer patients and inhibition of SNHG1 suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis[J]. Indian J Pathol Microbiol, 2020, 63(4): 575-580. doi: 10.4103/IJPM.IJPM_612_19
[8] Wang GF, Wen LN. LncRNA SNHG14 promotes proliferation of endometrial cancer through regulating microRNA-655-3p[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(20): 10410-10418. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/346250436_LncRNA_SNHG14_promotes_proliferation_of_endometrial_cancer_through_regulating_microRNA-655-3p
[9] Wei S, Sun S, Zhou X, et al. SNHG5 inhibits the progression of EMT through the ubiquitin-degradation of MTA2 in oesophageal cancer[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2021, 42(2): 315-326. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgaa110
[10] Chi JR, Yu ZH, Liu BW, et al. SNHG5 Promotes Breast Cancer Proliferation by Sponging the miR-154-5p/PCNA Axis[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2019, 17: 138-149. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.013
[11] Zhao L, Han T, Li Y, et al. The lncRNA SNHG5/miR-32 axis regulates gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting KLF4[J]. FASEB J, 2017, 31(3): 893-903. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600994R
[12] Zhao L, Guo H, Zhou B, et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 suppresses gastric cancer progression by trapping MTA2 in the cytosol[J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35(44): 5770-5780. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.110
[13] Chen L, Gong X, Huang M. YY1-Activated Long Noncoding RNA SNHG5 Promotes Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation Through p38/MAPK Signaling Pathway[J]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2019, 34(9): 589-596. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2019.2779
[14] Meng X, Deng Y, Lv Z, et al. LncRNA SNHG5 Promotes Proliferation of Glioma by Regulating miR-205-5p/ZEB2 Axis[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 11487-11496. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S228439
[15] Li X, Chen SH, Zeng JW. MiR-421 Is Overexpressed and Promotes Cell Proliferation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer[J]. Med Princ Pract, 2020, 29(1): 80-89. doi: 10.1159/000503020
[16] Xue L, Yang D. MiR-421 inhibited proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting MTA1[J]. J BUON, 2018, 23(6): 1633-1639. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30610787
[17] Meng D, Yang S, Wan X, et al. A transcriptional target of androgen receptor, miR-421 regulates proliferation and metabolism of prostate cancer cells[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2016, 73: 30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.01.018
[18] Liu L, Cui S, Zhang R, et al. MiR-421 inhibits the malignant phenotype in glioma by directly targeting MEF2D[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2017, 7(4): 857-868. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28469958
[19] Meng Q, Li S, Liu Y, et al. Circular RNA circSCAF11 Accelerates the Glioma Tumorigenesis through the miR-421/SP1/VEGFA Axis[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2019, 17: 669-677. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.06.022
[20] Zhao Y, Li Y, Ma Y, et al. Myocyte enhancer factor 2D promotes tumorigenicity in malignant glioma cells[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(1): 601-610. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3791-6



 下载:
下载: