Relationship of LncRNA AC010145.4 Expression with Prognosis and Chemoresistance of Small Cell Lung Cancer
-
摘要:目的
探讨LncRNA AC010145.4在小细胞肺癌患者组织中的表达及其与患者化疗敏感度和预后的关系。
方法应用实时荧光定量PCR法检测67例SCLC、27例癌旁及40例正常肺组织中LncRNA AC010145.4的表达,采用χ2检验分析LncRNA AC010145.4表达与SCLC患者临床病理特征的关系,Kaplan-Meier法分析LncRNA AC010145.4表达与SCLC患者生存时间的关系,单因素及多因素分析影响SCLC预后的因素。
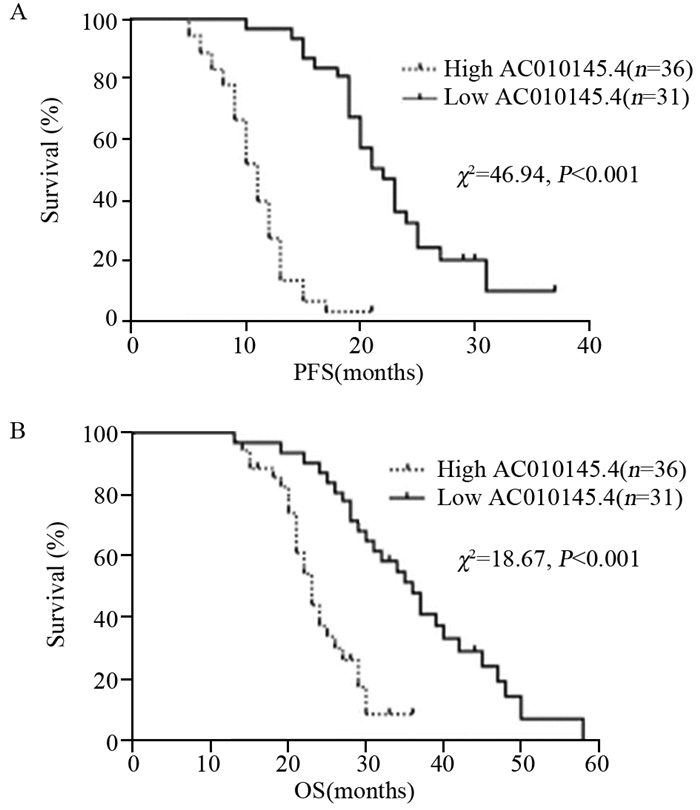
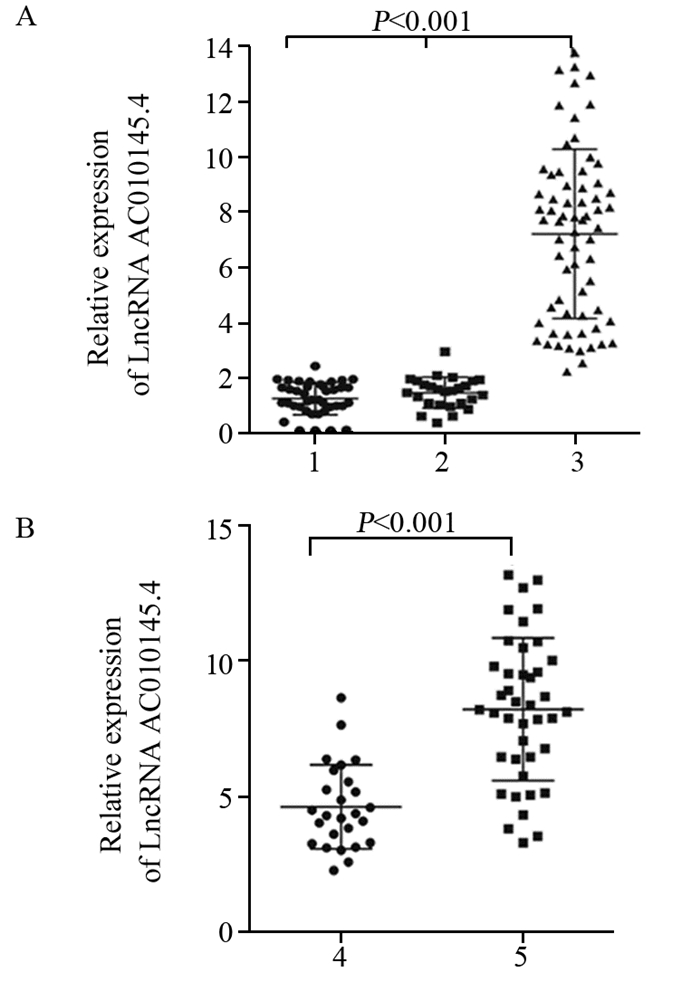
结果SCLC组织中LncRNA AC010145.4的表达水平明显高于癌旁组织及正常肺组织(均P < 0.001)。LncRNA AC010145.4在化疗耐药患者中的表达明显高于化疗敏感者(P < 0.05);LncRNA AC010145.4表达与SCLC患者的性别、年龄无关,而与疾病分期、淋巴结转移、远处转移、化疗耐药相关(均P < 0.05)。高表达LncRNA AC010145.4患者的总生存时间及无进展生存时间均短于低表达者(均P < 0.001)。单因素及多因素分析发现LncRNA AC010145.4表达、疾病分期、远处转移是SCLC患者独立的预后因素(均P < 0.05)。
结论LncRNA AC010145.4参与调节SCLC的发生和发展,可能是潜在的SCLC患者预后评估的生物标志物。
-
关键词:
- 小细胞肺癌 /
- 长链非编码RNA /
- LncRNA AC010145.4 /
- 预后
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the expression of long non-coding RNA AC010145.4 (LncRNA AC010145.4) and its relationship with prognosis and chemoresistance of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients.
MethodsThe expression of LncRNA AC010145.4 in 67 cases of SCLC tissues, 27 cases of para-cancerous tissues and 40 cases of normal lung tissues were detected by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR. The relationship of LncRNA AC010145.4 expression with clinicopathological characteristics was analysed by χ2 test. The relationship between AC010145.4 expression and survival time of SCLC patients were analyzed by Kaplan-Meier analysis. Univariate and multivariate analysis were used to analyze prognosis factor of SCLC.
ResultsThe expression level of LncRNA AC010145.4 in SCLC tissues was higher than those in para-cancerous tissues and normal lung tissues (all P < 0.001). The expression of LncRNA AC010145.4 was significantly higher in chemoresistance patients than that in chemosensitive patients (P < 0.05). LncRNA AC010145.4 expression was positively correlated with disease stage, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, chemosensitivity (all P < 0.05). The overall survival time and progression-free survival time of the patients with high LncRNA AC010145.4 expression were shorter than those with low LncRNA AC010145.4 expression (all P < 0.001). LncRNA AC010145.4 expression, disease stage and distant metastasis were independent prognostic factors (all P < 0.05).
ConclusionLncRNA AC010145.4 is involved in the occurrence and development of SCLC, and may be used as a molecular marker for the prognosis evaluation of SCLC patients.
-
Key words:
- Small cell lung cancer /
- Lnc RNA /
- LncRNA AC010145.4 /
- Prognosis
-
-
表 1 LncRNA AC010145.4表达与小细胞肺癌患者临床病理特征间的关系
Table 1 Relationship between LncRNA AC010145.4 expression and clinicopathological characteristics of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients

表 2 单因素和多因素分析影响小细胞肺癌患者OS的临床病理因素
Table 2 Univariate and multivariate analysis of clinicopathological features for OS of SCLC patients

-
[1] Butler KM, Rayens MK, Wiggins AT, et al. Association of smoking in the home with lung cancer worry, perceived risk, and synergistic risk[J]. Oncol Nurs Forum, 2017, 44(2):E55-63.
[2] Caswell G, Seymour J, Crosby V, et al. Lung cancer diagnosed following an emergency admission:exploring patient and carer perspectives on delay in seeking help[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2017, 25(7):2259-66. doi: 10.1007/s00520-017-3633-8
[3] Huang J, Peng J, Guo L. Non-coding RNA:a new tool for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy of small cell lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2015, 10(1):28-37. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000394
[4] Park S, Lee E, Rhee S, et al. Correlation between semi-quantitative (18) F-FDG PET/CT parameters and Ki-67 expression in small cell lung cancer[J]. Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2016, 50(1):24-30. doi: 10.1007/s13139-015-0363-z
[5] Xiao F, Bai Y, Chen Z, et al. Downregulation of HOXA1 gene affects small cell lung cancer cell survival and chemoresistance under the regulation of miR-100[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2014, 50(8):1541-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.01.024
[6] Haixia P, Yifeng B, and Honglin H. Role and clinical significance of RLIP76 in regulation of multi-drug resistance of small cell lung cancer[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2015, 37(4):266-71. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26462890
[7] Luo S, Bai Y, Lan H. Influence of interference of WIG-1 on the multi-drug resistance in small cell lung cancer[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2014, 36(10):733-8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25567302
[8] Williamson L, Saponaro M, Boeing S, et al. UV Irradiation Induces a Non-coding RNA that Functionally Opposes the Protein Encoded by the Same Gene[J]. Cell, 2017, 168(5):843-55. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.019
[9] Zhuo C, Hou W, Hu L, et al. Genomic editing of non-coding rna genes with crispr/cas9 ushers in a potential novel approach to study and treat schizophrenia[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2017, 10:28. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00028/full
[10] Jin Y, Cui Z, Li X, et al. Upregulation of long non-coding RNA PlncRNA-1 promotes proliferation and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(16):26090-9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5432240/
[11] Li H, Jiang X, Niu X. Long Non-Coding RNA Reprogramming (ROR) Promotes Cell Proliferation in Colorectal Cancer via Affecting P53[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2017, 23:919-28. doi: 10.12659/MSM.903462
[12] Qi X, Shao M, Sun H, et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG14 promotes microglia activation by regulating miR-145-5p/PLA2G4A in cerebral infarction[J]. Neuroscience, 2017, 348:98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.02.002
[13] Huang NS, Chi YY, Xue JY, et al. Long non-coding RNA metastasis associated in lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1(MALAT1) interacts with estrogen receptor and predicted poor survival in breast cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(25):37957-65. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v7i25
[14] Zhou C, Ye L, Jiang C, et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR, a hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha activated driver of malignancy, enhances hypoxic cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(12):9179-88. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3453-8
[15] Qiu M, Xu Y, Yang X, et al. CCAT2 is a lung adenocarcinoma-specific long non-coding RNA and promotes invasion of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35(6):5375-80. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-1700-z
[16] Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, et al. A critical role for the long non-coding RNA GAS5 in proliferation and apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2015, 54(Suppl 1):E1-12. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24357161
[17] Niu Y, Ma F, Huang W, et al. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 is involved in cell growth and chemoresistance of small cell lung cancer by regulating LIMK2b via EZH2[J]. Mol Cancer, 2017, 16(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0575-6
[18] Huang C, Liu S, Wang H, et al. LncRNA PVT1 overexpression is a poor prognostic biomarker and regulates migration and invasion in small cell lung cancer[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2016, 8(11):5025-34. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5126345/



 下载:
下载: