Effect of Hypoxia on Expression of HIF-1α, GLUT-1 and MMP-2 in Laryngeal Carcinoma Cell Line Hep-2
-
摘要:目的
探讨缺氧对喉癌Hep-2细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭以及缺氧诱导因子-1α(HIF-1α)、葡萄糖转运蛋白-1(GLUT-1)和基质金属蛋白酶-2(MMP-2)表达的影响。
方法MTT法检测缺氧不同时间点细胞增殖状况;Transwell和划痕实验分别检测缺氧对喉癌Hep-2细胞侵袭和迁移能力的影响;Western blot和实时定量反转录聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)检测缺氧后不同时间点HIF-1α、GLUT-1、MMP-2蛋白及mRNA表达的情况。
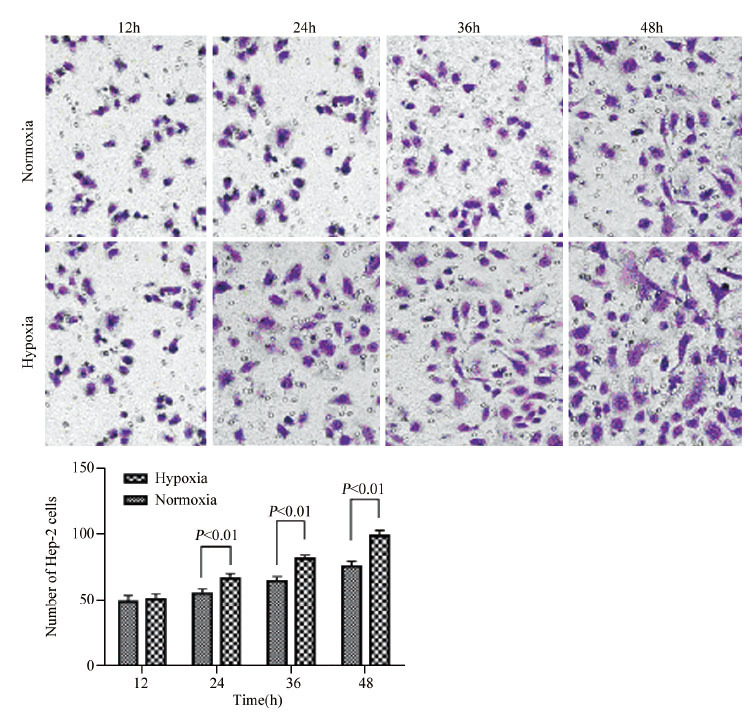
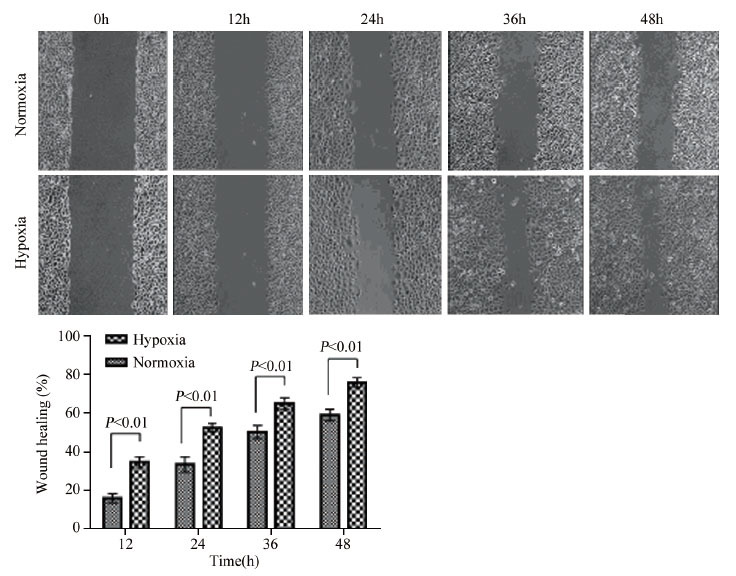
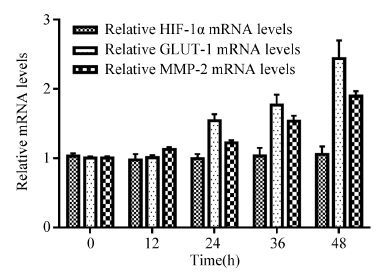
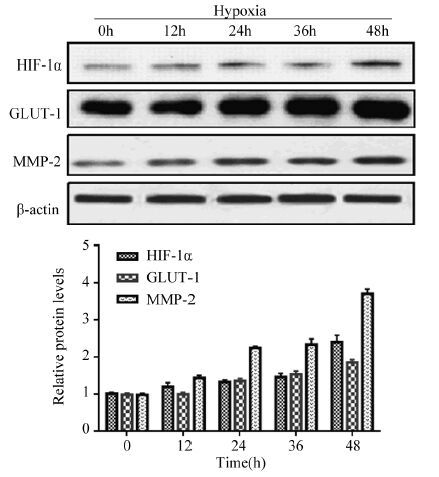
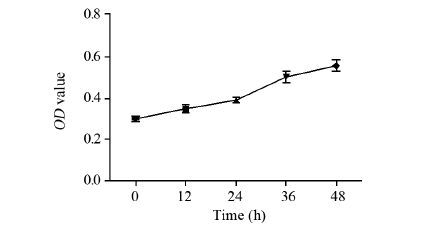
结果在缺氧条件下(1%O2、5%CO2和94%N2), Hep-2细胞的存活率随缺氧时间的延长逐渐升高, 迁移和侵袭能力增强;随缺氧时间延长, Hep-2细胞HIF-1α蛋白表达水平明显增加, mRNA水平变化不明显;随缺氧时间延长, GLUT-1、MMP-2的mRNA水平和蛋白水平均明显增加。
结论缺氧环境下, 喉癌肿瘤细胞通过上调HIF-1α、GLUT-1、MMP-2的表达, 强化其增殖、侵袭、转移的能力, 促进喉癌的发展。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate cell proliferation, migration, invasion and the expression of HIF-1α, GLUT-1, MMP-2 in laryngeal carcinoma cell line Hep-2 under hypoxia.
MethodsMTT assay was performed to investigate the proliferation of Hep-2 cells under hypoxic conditions; the invasion ability of Hep-2 cells was determined by Transwell assay; the migration ability of Hep-2 cells was determined by wound healing assay; the mRNA and protein expression of HIF-1α, MMP-2 and GLUT-1 were detected by Western blot and real-time PCR at various time points under hypoxia.
ResultsUnder the hypoxia(1%O2, 5%CO2 and 94%N2), the growth activity of Hep-2 cell line was enhanced with the time prolonged, and the migration and invasion abilities of Hep-2 cell were enhanced. The protein expression of HIF-1α in the hypoxia was increased than that in the normoxia, however, HIF-1α mRNA levels had no significant difference between hypoxia and normoxia. The protein and mRNA expression of GLUT-1 and MMP-2 were increased in hypoxic conditions than those in the normoxia.
ConclusionHypoxic conditions may promote the protein expressions of HIF-1α, GLUT-1 and MMP-2 in laryngeal carcinoma cell line Hep-2; the overexpression of three proteins may have contributed to the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of laryngeal carcinoma cells.
-
-
-
[1] 孔维佳.《耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学》[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010: 460. Kong WJ. Otorhinolaryngology-head and neck surgery[M]. 2nd Edition. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2010: 460.
[1] 孔维佳.《耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学》[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出 版社, 2010: 460. [Kong WJ. Otorhinolaryngology-head and neck surgery[M]. 2nd Edition. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2010: 460.] [2] Weljie AM, Jirik FR. Hypoxia induced metabolic shifts in cancer cells: moving beyond the Warburg effect[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2011, 43(7): 981-9. [2] Weljie AM, Jirik FR. Hypoxia induced metabolic shifts in cancer cells: moving beyond the Warburg effect[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2011, 43(7): 981-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.08.009
[3] Yu L, Liu Y, Cui Y. Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and its relationship to apoptosis and proliferation in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2004, 24(6): 636-8. doi: 10.1007/BF02911379
[3] Yu L, Liu Y, Cui Y. Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and its relationship to apoptosis and proliferation in human laryn geal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2004, 24(6): 636-8. [4] Wu XH, Chen SP, Mao JY, et al. Expression and significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and glucose transporter-1 in laryngeal carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2013, 5(1): 261-6. [4] Wu XH, Chen SP, Mao JY, et al. Expression and significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and glucose transporter-1 in laryngealcarcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2013, 5(1): 261-6.
[5] Lotfi A, Mohammadi G, Saniee L, et al. Serum Level of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in Patients with Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Clinical Significance[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2015, 16(15): 6749-51. [5] Lotfi A, Mohammadi G, Saniee L, et al. Serum Level of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in Patients with Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Clinical Significance[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2015, 16(15): 6749-51. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.15.6749
[6] Gatenby RA, Smallbone K, Maini PK, et al. Cellular adaptations to hypoxia and acidosis during somatic evolution of breast cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2007, 97(5): 646-53. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603922
[6] Gatenby RA, Smallbone K, Maini PK, et al. Cellular adaptations to hypoxia and acidosis during somatic evolution of breast cancer [J] Br J Cancer, 2007, 97(5): 646-53. [7] Zimna A, KurpiszM. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 in Physiological and Pathophysiological Angiogenesis: Applications and Therapies[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2015, 2015: 549412. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1597158509&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[7] Zimna A, KurpiszM. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 in Physiological and Pathophysiological Angiogenesis: Applications and Therapies[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2015, 2015: 549412. [8] 徐凌, 王锋, 卫巍, 等. 低氧对人肝癌HepG2细胞中HIF-lα及MIR-210表达的影响[J]. 肿瘤, 2011, 31(6): 502-7. Xu L, Wang F, Wei W, et al. Effects of hypoxia on the expressions of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and miR-210 in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells[J]. Zhong Liu, 2011, 31(6): 502-7.
[8] 徐凌, 王锋, 卫巍, 等. 低氧对人肝癌HepG2细胞中HIF-lα及 MIR-210表达的影响[J]. 肿瘤, 2011, 31(6): 502-7. [Xu L, Wang F, Wei W, et al. Effects of hypoxia on the expressions of hypoxiainducible factor-1 alpha and miR-210 in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells[J]. Zhong Liu, 2011, 31(6): 502-7.] [9] Bao YY, Zhou SH, Fan J, et al. Anticancer mechanism of apigenin and the implications of GLUT-1 expression in head and neck cancers[J]. Future Oncol, 2013, 9(9): 1353-64. doi: 10.2217/fon.13.84
[9] Bao YY, Zhou SH, Fan J, et al. Anticancer mechanism of apigenin and the implications of GLUT-1 expression in head and neck cancers[J]. Future Oncol, 2013, 9(9): 1353-64. [10] Eckert AW, Kappler M, Schubert J, et al. Correlation of expression of hypoxia-related proteins with prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2012, 16(2): 189-96. [10] Eckert AW, Kappler M, Schubert J, et al. Correlation of expression of hypoxia-related proteins with prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2012, 16(2): 189-96. doi: 10.1007/s10006-012-0335-8
[11] Hayashi M, Sakata M, Takeda T, et al. Induction of glucose transportor-1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha under hypoxic conditions in trophoblast derived cells[J]. J Endocrinol, 2004, 183(1): 145-54. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.05599
[11] Hayashi M, Sakata M, Takeda T, et al. Induction of glucose transportor-1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha under hypoxic conditions in trophoblast derived cells[J]. J Endocrinol, 2004, 183(1): 145-54. [12] Behrooz A, Ismail-Beigi F. Dual control of glutl glucose transporter gene expression by hypoxia and by inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation[J]. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272(9): 5555-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.9.5555
[12] Behrooz A, Ismail-Beigi F. Dual control of glutl glucose transporter gene expression by hypoxia and by inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation[J]. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272(9): 5555-62. [13] Corcoran ML, Hewitt RE, Kleiner DE Jr, et al. MMP-2: expression, activation and inhibition[J]. Enzyme Protein, 1996, 49(1-3): 7-19. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=166240207&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] Corcoran ML, Hewitt RE, Kleiner DE Jr, et al. MMP-2: expression, activation and inhibition[J]. Enzyme Protein, 1996, 49(1-3): 7-19. [14] Kondakova IV, Klisho EV, savenkova OV, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 as the factor of head and neck tumor metastasis[J]. Biomed Khim, 2008, 54(5): 555-60. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19105397
[14] Kondakova IV, Klisho EV, savenkova OV, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 as the factor of head and neck tumor metastasis[J]. Biomed Khim, 2008, 54(5): 555-60. [15] Jing SW, Wang YD, Kuroda M, et al. HIF-1α contributes to hypoxia-induced invasion and metastasis of esophageal carcinoma via inhibiting E-cadherin and promoting MMP-2 expression[J]. Acta Med Okayama, 2012, 66(5): 399-407. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2116120635&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[15] Jing SW, Wang YD, Kuroda M, et al. HIF-1α contributes to hypoxia-induced invasion and metastasis of esophageal carcinoma via inhibiting E-cadherin and promoting MMP-2 expression[J]. Acta Med Okayama, 2012, 66(5): 399-407.



 下载:
下载: